数字
1. 斐波那契数列
2. 求二进制中1的数目
3. N的阶乘中0的个数
4. 给定一个十进制正整数N,从1开始到N的所有整数中,出现1的个数。
比如N=2,则1,2中,出现了1个“1”
5. 快速寻找满足条件的两个数
快速找出一个数组中的两个数字,让这两个数组之和等于一个给定的值,假设这个数组中肯定存在至少一组符合要求的解
比如N=2,则1,2中,出现了1个“1”
快速找出一个数组中的两个数字,让这两个数组之和等于一个给定的值,假设这个数组中肯定存在至少一组符合要求的解
比如: how are you 转换成 you are how
#include <stdio.h>
void reverse(char * start, char *end){
if(NULL == start || NULL == end){
return;
}
char tmp;
while(start < end){
tmp = *start;
*start = *end;
*end = tmp;
start++;
end--;
}
}
//字反转
char * reverse_word(char * src){
if(NULL == src){
return NULL;
}
char *start = src;
char *end = src;
while(*end != '\0'){
end++;
}
end--;
reverse(start, end);
end = start;
while(*start != '\0'){
if(*start == ' '){ //指向空字符
start++;
end++;
continue;
}else if(*end == ' ' || *end == '\0'){ //end指向空格或字符串结尾
reverse(start, --end);//注意这里先 -- 再传end
start = ++end;//注意这里先++,再赋值给start
}else{ //end指向字符
end++;
}
}
return src;
}
int main(){
char src[] = "how are you";
char *p = reverse_word(src);
printf("%s\n", p);
}
#include <stdio.h>
int isValidValue(char *start, char *end){
int sum = 0;
while(start <= end){
if(*start < '0' || *start > '9'){
return -1;
}else{
sum = sum*10 + (*start - '0');
start++;
}
}
if(sum <0 || sum > 255){
return -1;
}
return 1;
}
int isValidFormat(char *src){
int num = 0;
int res = 0;
char *start = src;
char *end = src;
while(*start != '\0'){
printf("%s\n", start);
if(*start == '.'){
num++;
start++;
end++;
}else if(*end == '.' || *end == '\0'){
res = isValidValue(start, --end);
if(-1 == res){
return -1;
}else{
start = ++end;
}
}else{
end++;
}
}
if(3 != num){
return -1;
}
return 1;
}
int main(){
char *src = "24.1.2.4.1";
printf("%d\n", isValidFormat(src));
}
一个长字符串a,一个短字符串b,如何判断b中的字符都在a中?
#include <stdio.h>
#define N 10
char * strconnect(char src[], char des[]){
if(NULL == src || NULL == des){
return NULL;
}
char *p = des;
while(*des != '\0'){
des ++;
}
while(*src != '\0'){
*des = *src;
des ++;
src ++;
}
*des = '\0';
return p;
}
int main(){
char src[N] = "abcd";
char des[N] = "1234";
strconnect(src, des);
printf("%s\n", des);
}
#include <stdio.h>
char * strcopy(const char * src, char * des){
if(NULL == src || NULL == des){
return NULL;
}
char *p = des;
while(*src != '\0'){
*des = *src;
des++;
src++;
}
*des = '\0';
return p;
}
int main(){
const char *src = "abc";//src是指向 字符常量const char类型 的指针
char *des;
des = strcopy(src, des);//入参src与形参类型要一致,都是指向const char类型的指针
printf("%s\n", des);
}
字符串s1,s2,判断字符串s2能否被s1循环移位得到的字符串包含。例如,给定s1=‘AABCD’,s2=’CDAA’,则s1向右移动3位变长CDAAB,包含s2
字符串转整形
#include <stdio.h>
int str2int(char *str){
if(NULL == str){
return -1;
}
int sign = 1;
int des = 0;
if('-' == *str){
sign = -1;
str++;
}else if('+' == *str){
str++;
}
while(*str != '\0'){
if(*str >= '0' && *str <= '9'){
des = des*10 + (*str - '0');
str++;
}else{
return -1;
}
}
return sign * des;
}
int main(){
char *str = "-1234";
int des = str2int(str);
printf("%d\n", des);
}
整形转字符串,方法一
#include <stdio.h>
#define N 100
char * int2str(int src, char des[]){
if(0 == src){
return NULL;
}
int i=0, j=0;
char tmp[N];
while(src > 0){
tmp[i] = src % 10 + '0';
src = src / 10;
i++;
}
i--;
while(i >= 0){
des[j] = tmp[i];
i--;
j++;
}
des[j] = '\0';
return des;
}
int main(){
int src = 1234;
char des[N];
int2str(src, des);
printf("%s\n", des);
}
整形转字符串,方法二
#include <stdio.h>
char * int2str(int src, char *des){
if(0 == src){
return NULL;
}
char * tmp = des;
while(src > 0){
*tmp = src % 10 + '0';
tmp++;
src = src / 10;
}
*tmp = '\0';
char strTmp;
char *head = des;
char *end = --tmp;
while(head < end){
strTmp = *head;
*head = *end;
*end = strTmp;
head++;
end--;
}
return des;
}
int main(){
int src = 1234;
char * des;
des = int2str(src, des);//这里注意啊,需要把des传进去,不然int2str只能返回局部变量的指针,这种是错误的。
printf("%s\n", des);
}
把一个含有N个元素的数组,循环右移K位,要求时间复杂度为O(N),且只允许使用两个附加变量。
有一个无序,元素个数为2n的正整数数组,要求:如何能把这个数组分割成元素个数为n的两个数组,并使两个子数组的和最接近。
比如: how are you 转换成 you are how
一个长字符串a,一个短字符串b,如何判断b中的字符都在a中?
字符串s1,s2,判断字符串s2能否被s1循环移位得到的字符串包含。例如,给定s1=‘AABCD’,s2=’CDAA’,则s1向右移动3位变长CDAAB,包含s2
比如N=2,则1,2中,出现了1个“1”
快速找出一个数组中的两个数字,让这两个数组之和等于一个给定的值,假设这个数组中肯定存在至少一组符合要求的解
layout: post author: GoSaturn title: redis源码学习——事件(二) category: 源码学习 tag: [redis] —
本文主要梳理
文件事件处理流程
##整体流程
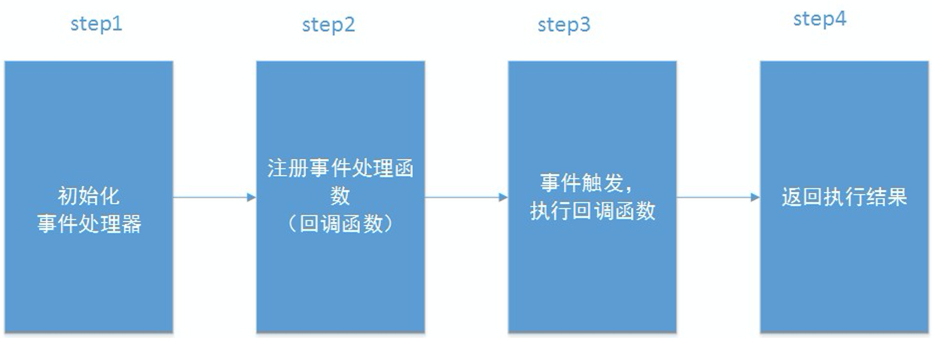
##流程详解 ###step1: 初始化事件处理器结构体
// redis.c/initServer()
//全局变量
struct redisServer server;
//初始化事件处理器结构体
server.el = aeCreateEventLoop(server.maxclients+REDIS_EVENTLOOP_FDSET_INCR);
**事件处理器结构体:**
<figure class="highlight"><pre><code class="language-c" data-lang="c"><span class="k">typedef</span> <span class="k">struct</span> <span class="n">aeEventLoop</span> <span class="p">{</span>
<span class="p">...</span>
<span class="c1">// 已注册的文件事件, events是aeFileEvent类型
</span> <span class="n">aeFileEvent</span> <span class="o">*</span><span class="n">events</span><span class="p">;</span>
<span class="p">...</span>
<span class="p">}</span> <span class="n">aeEventLoop</span><span class="p">;</span></code></pre></figure>
其中,**aeFileEvent结构体定义**如下:
<figure class="highlight"><pre><code class="language-c" data-lang="c"><span class="k">typedef</span> <span class="k">struct</span> <span class="n">aeFileEvent</span> <span class="p">{</span>
<span class="c1">// 监听事件类型掩码,
</span> <span class="c1">// 值可以是 AE_READABLE 或 AE_WRITABLE ,
</span> <span class="c1">// 或者 AE_READABLE | AE_WRITABLE
</span> <span class="kt">int</span> <span class="n">mask</span><span class="p">;</span> <span class="cm">/* one of AE_(READABLE|WRITABLE) */</span>
<span class="c1">// 读事件处理器,aeFileProc为函数指针
</span> <span class="n">aeFileProc</span> <span class="o">*</span><span class="n">rfileProc</span><span class="p">;</span>
<span class="c1">// 写事件处理器
</span> <span class="n">aeFileProc</span> <span class="o">*</span><span class="n">wfileProc</span><span class="p">;</span>
<span class="c1">// 多路复用库的私有数据
</span> <span class="kt">void</span> <span class="o">*</span><span class="n">clientData</span><span class="p">;</span>
<span class="p">}</span> <span class="n">aeFileEvent</span><span class="p">;</span></code></pre></figure>
**aeFileProc函数指针定义**如下:
<figure class="highlight"><pre><code class="language-c" data-lang="c"><span class="k">typedef</span> <span class="kt">void</span> <span class="n">aeFileProc</span><span class="p">(</span><span class="k">struct</span> <span class="n">aeEventLoop</span> <span class="o">*</span><span class="n">eventLoop</span><span class="p">,</span> <span class="kt">int</span> <span class="n">fd</span><span class="p">,</span> <span class="kt">void</span> <span class="o">*</span><span class="n">clientData</span><span class="p">,</span> <span class="kt">int</span> <span class="n">mask</span><span class="p">);</span></code></pre></figure>
在c语言中,`回调是通过函数指针实现的`。通过将回调函数地址 传递给 被调函数,从而实现回调。在这里,通过定义函数指针aeFileProc,由调用方实现具体的函数内容,在实际调用函数里,把aeFileProc实现函数的地址传进来。其实相当于定义一种接口,由调用方来实现该接口。
###step2: 注册事件处理函数
//redis.c/initServer()
// 为 TCP 连接关联连接应答(accept)处理器
// 用于接受并应答客户端的 connect() 调用
for (j = 0; j < server.ipfd_count; j++) {
if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el, server.ipfd[j], AE_READABLE,
acceptTcpHandler,NULL) == AE_ERR)
{
redisPanic(
"Unrecoverable error creating server.ipfd file event.");
}
}
// 为本地套接字关联应答处理器
if (server.sofd > 0 && aeCreateFileEvent(server.el,server.sofd,AE_READABLE,
acceptUnixHandler,NULL) == AE_ERR) redisPanic("Unrecoverable error creating server.sofd file event."); ``` 以TCP连接为例,说明注册流程。通过调用aeCreateFileEvent函数,把aeFilePrco函数指针的实现函数——acceptTcpHandler作为参数传进去。
aeCreateFileEvent函数如下:
//ae.c/aeCreateFileEvent()
int aeCreateFileEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, int mask,
aeFileProc *proc, void *clientData)
{
if (fd >= eventLoop->setsize) {
errno = ERANGE;
return AE_ERR;
}
if (fd >= eventLoop->setsize) return AE_ERR;
// 取出文件事件结构
aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[fd];//注意这里是引用!!! by gs
// 监听指定 fd 的指定事件
if (aeApiAddEvent(eventLoop, fd, mask) == -1)
return AE_ERR;
// 设置文件事件类型,以及事件的处理器
fe->mask |= mask;
//将事件处理器函数(回调函数)赋值给aeFileEvent结构体中对应的函数指针,其实就是赋值给aeEventLoop结构体中的events by gs
if (mask & AE_READABLE) fe->rfileProc = proc;
if (mask & AE_WRITABLE) fe->wfileProc = proc;
// 私有数据
fe->clientData = clientData;
// 如果有需要,更新事件处理器的最大 fd
if (fd > eventLoop->maxfd)
eventLoop->maxfd = fd;
return AE_OK;
}
函数说明如下: 1) aeApiAddEvent 以epoll为例,ae_epoll.c文件中,实现aeApiAddEvent接口,调用epoll系统函数,注册事件。 2)将aeFileProc *proc赋值给aeEventLoop *eventLoop中的events,完成回调函数注册。
###step3: 事件触发,执行回调函数
//ae.c/aeMain()
void aeMain(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
eventLoop->stop = 0;
while (!eventLoop->stop) {
// 如果有需要在事件处理前执行的函数,那么运行它
if (eventLoop->beforesleep != NULL)
eventLoop->beforesleep(eventLoop);
// 开始处理事件
aeProcessEvents(eventLoop, AE_ALL_EVENTS);
}
}
aeProcessEvents函数如下:
int aeProcessEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int flags)
{
...
// 处理文件事件,阻塞时间由 tvp 决定
numevents = aeApiPoll(eventLoop, tvp);//aeApiPoll获取已就绪事件by gs
for (j = 0; j < numevents; j++) {
// 从已就绪数组中获取事件
aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[eventLoop->fired[j].fd];
int mask = eventLoop->fired[j].mask;
int fd = eventLoop->fired[j].fd;
int rfired = 0;
// 读事件
if (fe->mask & mask & AE_READABLE) {
// rfired 确保读/写事件只能执行其中一个
rfired = 1;
fe->rfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask);//执行回调函数
}
// 写事件
if (fe->mask & mask & AE_WRITABLE) {
if (!rfired || fe->wfileProc != fe->rfileProc)
fe->wfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask);//执行回调函数
}
processed++;
}
...
}
执行回调函数acceptTcpHandle
//networking.c/acceptTcpHandler()
//创建TCP连接处理器
void acceptTcpHandler(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) {
int cport, cfd, max = MAX_ACCEPTS_PER_CALL;
char cip[REDIS_IP_STR_LEN];
REDIS_NOTUSED(el);
REDIS_NOTUSED(mask);
REDIS_NOTUSED(privdata);
while(max--) {
// accept 客户端连接
cfd = anetTcpAccept(server.neterr, fd, cip, sizeof(cip), &cport);
if (cfd == ANET_ERR) {
if (errno != EWOULDBLOCK)
redisLog(REDIS_WARNING,
"Accepting client connection: %s", server.neterr);
return;
}
redisLog(REDIS_VERBOSE,"Accepted %s:%d", cip, cport);
// 为客户端创建客户端状态(redisClient)
acceptCommonHandler(cfd,0);
}
}
主要步骤: 1) anetTcpAccept用于接收客户端连接,返回连接的fd; 2)acceptCommonHandle用于为每个客户端连接创建redisClient结构体。 anetTcpAccept函数:
//anet.c/anetTcpAccept()
//Tcp连接accept
int antTcpAccept(char *err, int s, char *ip, size_t ip_len, int *port) {
int fd;
struct sockaddr_storage sa;
socklen_t salen = sizeof(sa);
if ((fd = anetGenericAccept(err,s,(struct sockaddr*)&sa,&salen)) == -1)
return ANET_ERR;
if (sa.ss_family == AF_INET) {
struct sockaddr_in *s = (struct sockaddr_in *)&sa;
if (ip) inet_ntop(AF_INET,(void*)&(s->sin_addr),ip,ip_len);
if (port) *port = ntohs(s->sin_port);
} else {
struct sockaddr_in6 *s = (struct sockaddr_in6 *)&sa;
if (ip) inet_ntop(AF_INET6,(void*)&(s->sin6_addr),ip,ip_len);
if (port) *port = ntohs(s->sin6_port);
}
return fd;
}
anetGenericAccept函数:
static int anetGenericAccept(char *err, int s, struct sockaddr *sa, socklen_t *len) {
int fd;
while(1) {
fd = accept(s,sa,len);//系统调用accept函数,接收Tcp连接
if (fd == -1) {
if (errno == EINTR)
continue;
else {
anetSetError(err, "accept: %s", strerror(errno));
return ANET_ERR;
}
}
break;
}
return fd;
}
accept函数从连接请求队列中获取第一个连接,创建新的套接字,并返回fd。如果队列中无请求连接&套接字为阻塞方式,则accept函数阻塞调用进程直到新的连接出现;如果为非阻塞&无请求连接,则accept函数返回一个错误信息。
acceptCommonHandler函数:
//networking.c/acceptCommonHandler()
//处理tcp连接
static void acceptCommonHandler(int fd, int flags) {
// 创建客户端
redisClient *c;
if ((c = createClient(fd)) == NULL) {
redisLog(REDIS_WARNING,
"Error registering fd event for the new client: %s (fd=%d)",
strerror(errno),fd);
close(fd); /* May be already closed, just ignore errors */
return;
}
...
}
该函数主要调用createClient为连接创建客户端结构体。 createClient函数:
redisClient *createClient(int fd) {
// 分配空间
redisClient *c = zmalloc(sizeof(redisClient));
// 当 fd 不为 -1 时,创建带网络连接的客户端
// 如果 fd 为 -1 ,那么创建无网络连接的伪客户端
// 因为 Redis 的命令必须在客户端的上下文中使用,所以在执行 Lua 环境中的命令时需要用到这种伪终端
if (fd != -1) {
// 非阻塞
anetNonBlock(NULL,fd);
// 禁用 Nagle 算法
anetEnableTcpNoDelay(NULL,fd);
// 设置 keep alive
if (server.tcpkeepalive)
anetKeepAlive(NULL,fd,server.tcpkeepalive);
// 绑定读事件到事件 loop (开始接收命令请求)
if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el,fd,AE_READABLE,
readQueryFromClient, c) == AE_ERR)
{
close(fd);
zfree(c);
return NULL;
}
}
...
}
这里又一次调用aeCreateFileEvent函数,传入回调函数readQueryFromClient,用来处理该连接上的数据。 readQueryFromClient函数:
void readQueryFromClient(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) {
redisClient *c = (redisClient*) privdata;
...
// 设置服务器的当前客户端
server.current_client = c;
...
// 读入内容到查询缓存
nread = read(fd, c->querybuf+qblen, readlen);//读数据
...
// 从查询缓存重读取内容,创建参数,并执行命令
// 函数会执行到缓存中的所有内容都被处理完为止
processInputBuffer(c);//解析成命令
...
}
processInputBuffer函数:
//networking.c/processInputBuffer()
//处理客户端出入的命令
void processInputBuffer(redisClient *c) {
while(sdslen(c->querybuf)) {
...
// 将缓冲区中的内容转换成命令,以及命令参数
if (c->reqtype == REDIS_REQ_INLINE) {
if (processInlineBuffer(c) != REDIS_OK) break;
} else if (c->reqtype == REDIS_REQ_MULTIBULK) {
if (processMultibulkBuffer(c) != REDIS_OK) break;
} else {
redisPanic("Unknown request type");
}
/* Multibulk processing could see a <= 0 length. */
if (c->argc == 0) {
resetClient(c);
} else {
/* Only reset the client when the command was executed. */
// 执行命令,并重置客户端
if (processCommand(c) == REDIS_OK)
resetClient(c);
}
}
}
首先处理数据内容,解析成命令,然后调用processCommand函数执行命令。 processCommand函数:
//redis.c/processCommand()
int processCommand(redisClient *c){
...
// 查找命令,并进行命令合法性检查,以及命令参数个数检查
c->cmd = c->lastcmd = lookupCommand(c->argv[0]->ptr);
...
//执行命令
if (c->flags & REDIS_MULTI &&
c->cmd->proc != execCommand && c->cmd->proc != discardCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != multiCommand && c->cmd->proc != watchCommand)
{
// 在事务上下文中
// 除 EXEC 、 DISCARD 、 MULTI 和 WATCH 命令之外,其他所有命令都会被入队到事务队列中
queueMultiCommand(c);
addReply(c,shared.queued);
} else {
// 执行命令
call(c,REDIS_CALL_FULL);
c->woff = server.master_repl_offset;
// 处理那些解除了阻塞的键
if (listLength(server.ready_keys))
handleClientsBlockedOnLists();
}
return REDIS_OK;
}
调用call()执行命令。 call函数:
//redis.c/call()
//调用命令的实现函数,执行命令
void call(redisClient *c, int flags) {
...
// 执行实现函数
c->cmd->proc(c);
...
}
###step4: 回复请求 以mget命令为例,说明服务器是怎么返回命令结果的。
//t_string.c/mgetCommand()
void mgetCommand(redisClient *c) {
int j;
addReplyMultiBulkLen(c,c->argc-1);
// 查找并返回所有输入键的值
for (j = 1; j < c->argc; j++) {
// 查找键 c->argc[j] 的值
robj *o = lookupKeyRead(c->db,c->argv[j]);
if (o == NULL) {
// 值不存在,向客户端发送空回复
addReply(c,shared.nullbulk);
} else {
if (o->type != REDIS_STRING) {
// 值存在,但不是字符串类型
addReply(c,shared.nullbulk);
} else {
// 值存在,并且是字符串
addReplyBulk(c,o);
}
}
}
}
命令执行后,调用addReply函数,回复客户端。 addReply函数:
//networking.c/addReply()
void addReply(redisClient *c, robj *obj) {
// 为客户端安装写处理器到事件循环
if (prepareClientToWrite(c) != REDIS_OK) return;
...
}
在该函数中,调用prepareClientToWrite函数,注册写时间处理器。 prepareClientToWrite函数:
//networking.c/prepareClientToWrite()
int prepareClientToWrite(redisClient *c) {
...
// 一般情况,为客户端套接字安装写处理器到事件循环
if (c->bufpos == 0 && listLength(c->reply) == 0 &&
(c->replstate == REDIS_REPL_NONE ||
c->replstate == REDIS_REPL_ONLINE) &&
aeCreateFileEvent(server.el, c->fd, AE_WRITABLE,
sendReplyToClient, c) == AE_ERR) return REDIS_ERR;
return REDIS_OK;
}
调用aeCreateFileEvent函数,注册sendReplyToClient事件处理函数。 sendReplyToClient函数:
//networking.c/sendReplyToClient()
void sendReplyToClient(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) {
...
while(c->bufpos > 0 || listLength(c->reply)) {
if (c->bufpos > 0) {
...
//调用系统函数write写数据到fd
nwritten = write(fd,c->buf+c->sentlen,c->bufpos-c->sentlen);
...
}else{
...
//调用系统函数write写数据到fd
nwritten = write(fd, ((char*)o->ptr)+c->sentlen,objlen-c->sentlen);
...
}
}
...
}
##小结 如上,redis文件事件处理流程:
本文主要梳理
文件事件处理流程

// redis.c/initServer()
//全局变量
struct redisServer server;
//初始化事件处理器结构体
server.el = aeCreateEventLoop(server.maxclients+REDIS_EVENTLOOP_FDSET_INCR);
事件处理器结构体:
typedef struct aeEventLoop {
...
// 已注册的文件事件, events是aeFileEvent类型
aeFileEvent *events;
...
} aeEventLoop;
其中,aeFileEvent结构体定义如下:
typedef struct aeFileEvent {
// 监听事件类型掩码,
// 值可以是 AE_READABLE 或 AE_WRITABLE ,
// 或者 AE_READABLE | AE_WRITABLE
int mask; /* one of AE_(READABLE|WRITABLE) */
// 读事件处理器,aeFileProc为函数指针
aeFileProc *rfileProc;
// 写事件处理器
aeFileProc *wfileProc;
// 多路复用库的私有数据
void *clientData;
} aeFileEvent;
aeFileProc函数指针定义如下:
typedef void aeFileProc(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, void *clientData, int mask);
在c语言中,回调是通过函数指针实现的。
通过将回调函数地址 传递给 被调函数,从而实现回调。在这里,通过定义函数指针aeFileProc,由调用方实现具体的函数内容,在实际调用函数里,把aeFileProc实现函数的地址传进来。其实相当于定义一种接口,由调用方来实现该接口。
//redis.c/initServer()
// 为 TCP 连接关联连接应答(accept)处理器
// 用于接受并应答客户端的 connect() 调用
for (j = 0; j < server.ipfd_count; j++) {
if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el, server.ipfd[j], AE_READABLE,
acceptTcpHandler,NULL) == AE_ERR)
{
redisPanic(
"Unrecoverable error creating server.ipfd file event.");
}
}
// 为本地套接字关联应答处理器
if (server.sofd > 0 && aeCreateFileEvent(server.el,server.sofd,AE_READABLE,
acceptUnixHandler,NULL) == AE_ERR) redisPanic("Unrecoverable error creating server.sofd file event.");
以TCP连接为例,说明注册流程。通过调用aeCreateFileEvent函数,把aeFilePrco函数指针的实现函数——acceptTcpHandler作为参数传进去。
aeCreateFileEvent函数如下:
//ae.c/aeCreateFileEvent()
int aeCreateFileEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, int mask,
aeFileProc *proc, void *clientData)
{
if (fd >= eventLoop->setsize) {
errno = ERANGE;
return AE_ERR;
}
if (fd >= eventLoop->setsize) return AE_ERR;
// 取出文件事件结构
aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[fd];//注意这里是引用!!! by gs
// 监听指定 fd 的指定事件
if (aeApiAddEvent(eventLoop, fd, mask) == -1)
return AE_ERR;
// 设置文件事件类型,以及事件的处理器
fe->mask |= mask;
//将事件处理器函数(回调函数)赋值给aeFileEvent结构体中对应的函数指针,其实就是赋值给aeEventLoop结构体中的events by gs
if (mask & AE_READABLE) fe->rfileProc = proc;
if (mask & AE_WRITABLE) fe->wfileProc = proc;
// 私有数据
fe->clientData = clientData;
// 如果有需要,更新事件处理器的最大 fd
if (fd > eventLoop->maxfd)
eventLoop->maxfd = fd;
return AE_OK;
}
函数说明如下:
1) aeApiAddEvent
以epoll为例,ae_epoll.c文件中,实现aeApiAddEvent接口,调用epoll系统函数,注册事件。
2)将aeFileProc *proc赋值给aeEventLoop *eventLoop中的events,完成回调函数注册。
//ae.c/aeMain()
void aeMain(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
eventLoop->stop = 0;
while (!eventLoop->stop) {
// 如果有需要在事件处理前执行的函数,那么运行它
if (eventLoop->beforesleep != NULL)
eventLoop->beforesleep(eventLoop);
// 开始处理事件
aeProcessEvents(eventLoop, AE_ALL_EVENTS);
}
}
aeProcessEvents函数如下:
int aeProcessEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int flags)
{
...
// 处理文件事件,阻塞时间由 tvp 决定
numevents = aeApiPoll(eventLoop, tvp);//aeApiPoll获取已就绪事件by gs
for (j = 0; j < numevents; j++) {
// 从已就绪数组中获取事件
aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[eventLoop->fired[j].fd];
int mask = eventLoop->fired[j].mask;
int fd = eventLoop->fired[j].fd;
int rfired = 0;
// 读事件
if (fe->mask & mask & AE_READABLE) {
// rfired 确保读/写事件只能执行其中一个
rfired = 1;
fe->rfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask);//执行回调函数
}
// 写事件
if (fe->mask & mask & AE_WRITABLE) {
if (!rfired || fe->wfileProc != fe->rfileProc)
fe->wfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask);//执行回调函数
}
processed++;
}
...
}
执行回调函数acceptTcpHandle
//networking.c/acceptTcpHandler()
//创建TCP连接处理器
void acceptTcpHandler(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) {
int cport, cfd, max = MAX_ACCEPTS_PER_CALL;
char cip[REDIS_IP_STR_LEN];
REDIS_NOTUSED(el);
REDIS_NOTUSED(mask);
REDIS_NOTUSED(privdata);
while(max--) {
// accept 客户端连接
cfd = anetTcpAccept(server.neterr, fd, cip, sizeof(cip), &cport);
if (cfd == ANET_ERR) {
if (errno != EWOULDBLOCK)
redisLog(REDIS_WARNING,
"Accepting client connection: %s", server.neterr);
return;
}
redisLog(REDIS_VERBOSE,"Accepted %s:%d", cip, cport);
// 为客户端创建客户端状态(redisClient)
acceptCommonHandler(cfd,0);
}
}
主要步骤:
1) anetTcpAccept用于接收客户端连接,返回连接的fd;
2)acceptCommonHandle用于为每个客户端连接创建redisClient结构体。
anetTcpAccept函数:
//anet.c/anetTcpAccept()
//Tcp连接accept
int antTcpAccept(char *err, int s, char *ip, size_t ip_len, int *port) {
int fd;
struct sockaddr_storage sa;
socklen_t salen = sizeof(sa);
if ((fd = anetGenericAccept(err,s,(struct sockaddr*)&sa,&salen)) == -1)
return ANET_ERR;
if (sa.ss_family == AF_INET) {
struct sockaddr_in *s = (struct sockaddr_in *)&sa;
if (ip) inet_ntop(AF_INET,(void*)&(s->sin_addr),ip,ip_len);
if (port) *port = ntohs(s->sin_port);
} else {
struct sockaddr_in6 *s = (struct sockaddr_in6 *)&sa;
if (ip) inet_ntop(AF_INET6,(void*)&(s->sin6_addr),ip,ip_len);
if (port) *port = ntohs(s->sin6_port);
}
return fd;
}
anetGenericAccept函数:
static int anetGenericAccept(char *err, int s, struct sockaddr *sa, socklen_t *len) {
int fd;
while(1) {
fd = accept(s,sa,len);//系统调用accept函数,接收Tcp连接
if (fd == -1) {
if (errno == EINTR)
continue;
else {
anetSetError(err, "accept: %s", strerror(errno));
return ANET_ERR;
}
}
break;
}
return fd;
}
accept函数从连接请求队列中获取第一个连接,创建新的套接字,并返回fd。如果队列中无请求连接&套接字为阻塞方式,则accept函数阻塞调用进程直到新的连接出现;如果为非阻塞&无请求连接,则accept函数返回一个错误信息。
acceptCommonHandler函数:
//networking.c/acceptCommonHandler()
//处理tcp连接
static void acceptCommonHandler(int fd, int flags) {
// 创建客户端
redisClient *c;
if ((c = createClient(fd)) == NULL) {
redisLog(REDIS_WARNING,
"Error registering fd event for the new client: %s (fd=%d)",
strerror(errno),fd);
close(fd); /* May be already closed, just ignore errors */
return;
}
...
}
该函数主要调用createClient为连接创建客户端结构体。
createClient函数:
redisClient *createClient(int fd) {
// 分配空间
redisClient *c = zmalloc(sizeof(redisClient));
// 当 fd 不为 -1 时,创建带网络连接的客户端
// 如果 fd 为 -1 ,那么创建无网络连接的伪客户端
// 因为 Redis 的命令必须在客户端的上下文中使用,所以在执行 Lua 环境中的命令时需要用到这种伪终端
if (fd != -1) {
// 非阻塞
anetNonBlock(NULL,fd);
// 禁用 Nagle 算法
anetEnableTcpNoDelay(NULL,fd);
// 设置 keep alive
if (server.tcpkeepalive)
anetKeepAlive(NULL,fd,server.tcpkeepalive);
// 绑定读事件到事件 loop (开始接收命令请求)
if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el,fd,AE_READABLE,
readQueryFromClient, c) == AE_ERR)
{
close(fd);
zfree(c);
return NULL;
}
}
...
}
这里又一次调用aeCreateFileEvent函数,传入回调函数readQueryFromClient,用来处理该连接上的数据。
readQueryFromClient函数:
void readQueryFromClient(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) {
redisClient *c = (redisClient*) privdata;
...
// 设置服务器的当前客户端
server.current_client = c;
...
// 读入内容到查询缓存
nread = read(fd, c->querybuf+qblen, readlen);//读数据
...
// 从查询缓存重读取内容,创建参数,并执行命令
// 函数会执行到缓存中的所有内容都被处理完为止
processInputBuffer(c);//解析成命令
...
}
processInputBuffer函数:
//networking.c/processInputBuffer()
//处理客户端出入的命令
void processInputBuffer(redisClient *c) {
while(sdslen(c->querybuf)) {
...
// 将缓冲区中的内容转换成命令,以及命令参数
if (c->reqtype == REDIS_REQ_INLINE) {
if (processInlineBuffer(c) != REDIS_OK) break;
} else if (c->reqtype == REDIS_REQ_MULTIBULK) {
if (processMultibulkBuffer(c) != REDIS_OK) break;
} else {
redisPanic("Unknown request type");
}
/* Multibulk processing could see a <= 0 length. */
if (c->argc == 0) {
resetClient(c);
} else {
/* Only reset the client when the command was executed. */
// 执行命令,并重置客户端
if (processCommand(c) == REDIS_OK)
resetClient(c);
}
}
}
首先处理数据内容,解析成命令,然后调用processCommand函数执行命令。
processCommand函数:
//redis.c/processCommand()
int processCommand(redisClient *c){
...
// 查找命令,并进行命令合法性检查,以及命令参数个数检查
c->cmd = c->lastcmd = lookupCommand(c->argv[0]->ptr);
...
//执行命令
if (c->flags & REDIS_MULTI &&
c->cmd->proc != execCommand && c->cmd->proc != discardCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != multiCommand && c->cmd->proc != watchCommand)
{
// 在事务上下文中
// 除 EXEC 、 DISCARD 、 MULTI 和 WATCH 命令之外,其他所有命令都会被入队到事务队列中
queueMultiCommand(c);
addReply(c,shared.queued);
} else {
// 执行命令
call(c,REDIS_CALL_FULL);
c->woff = server.master_repl_offset;
// 处理那些解除了阻塞的键
if (listLength(server.ready_keys))
handleClientsBlockedOnLists();
}
return REDIS_OK;
}
调用call()执行命令。
call函数:
//redis.c/call()
//调用命令的实现函数,执行命令
void call(redisClient *c, int flags) {
...
// 执行实现函数
c->cmd->proc(c);
...
}
以mget命令为例,说明服务器是怎么返回命令结果的。
//t_string.c/mgetCommand()
void mgetCommand(redisClient *c) {
int j;
addReplyMultiBulkLen(c,c->argc-1);
// 查找并返回所有输入键的值
for (j = 1; j < c->argc; j++) {
// 查找键 c->argc[j] 的值
robj *o = lookupKeyRead(c->db,c->argv[j]);
if (o == NULL) {
// 值不存在,向客户端发送空回复
addReply(c,shared.nullbulk);
} else {
if (o->type != REDIS_STRING) {
// 值存在,但不是字符串类型
addReply(c,shared.nullbulk);
} else {
// 值存在,并且是字符串
addReplyBulk(c,o);
}
}
}
}
命令执行后,调用addReply函数,回复客户端。
addReply函数:
//networking.c/addReply()
void addReply(redisClient *c, robj *obj) {
// 为客户端安装写处理器到事件循环
if (prepareClientToWrite(c) != REDIS_OK) return;
...
}
在该函数中,调用prepareClientToWrite函数,注册写时间处理器。
prepareClientToWrite函数:
//networking.c/prepareClientToWrite()
int prepareClientToWrite(redisClient *c) {
...
// 一般情况,为客户端套接字安装写处理器到事件循环
if (c->bufpos == 0 && listLength(c->reply) == 0 &&
(c->replstate == REDIS_REPL_NONE ||
c->replstate == REDIS_REPL_ONLINE) &&
aeCreateFileEvent(server.el, c->fd, AE_WRITABLE,
sendReplyToClient, c) == AE_ERR) return REDIS_ERR;
return REDIS_OK;
}
调用aeCreateFileEvent函数,注册sendReplyToClient事件处理函数。
sendReplyToClient函数:
//networking.c/sendReplyToClient()
void sendReplyToClient(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) {
...
while(c->bufpos > 0 || listLength(c->reply)) {
if (c->bufpos > 0) {
...
//调用系统函数write写数据到fd
nwritten = write(fd,c->buf+c->sentlen,c->bufpos-c->sentlen);
...
}else{
...
//调用系统函数write写数据到fd
nwritten = write(fd, ((char*)o->ptr)+c->sentlen,objlen-c->sentlen);
...
}
}
...
}
如上,redis文件事件处理流程: